
Discovery of the novel propagation of monocyte exhaustion: Exhausted monocytes can propagate their dysfunctional pathogenic exhaustion to neighboring cells through inter-cellular communications in vivo and ex vivo
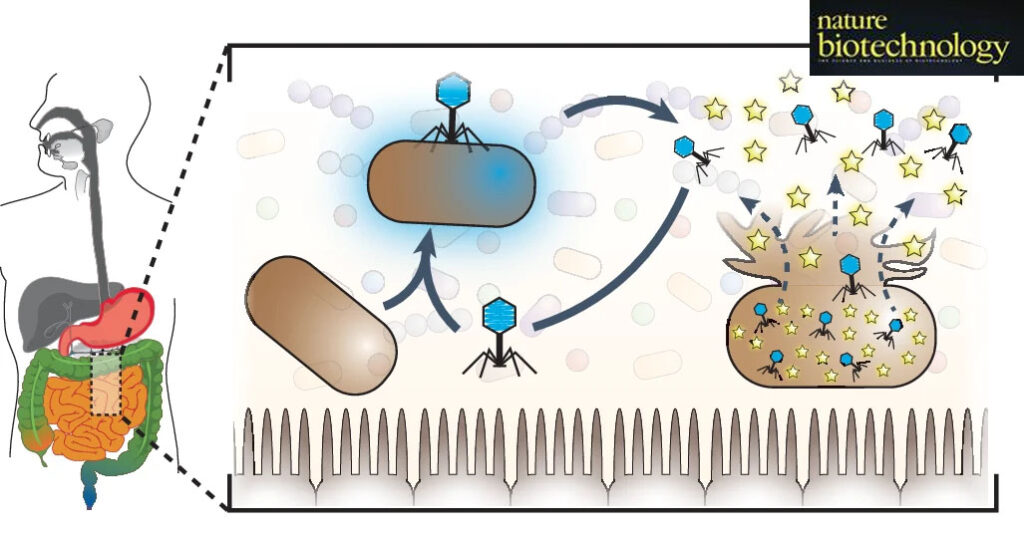
The introduction of an engineered bacterial phage producing SerpinB1 can rejuvenate host neutrophils and improve gut health.
TRAM discovered as a generic sensor for innate stress signals initiating low-grade inflammation memory in monocytes
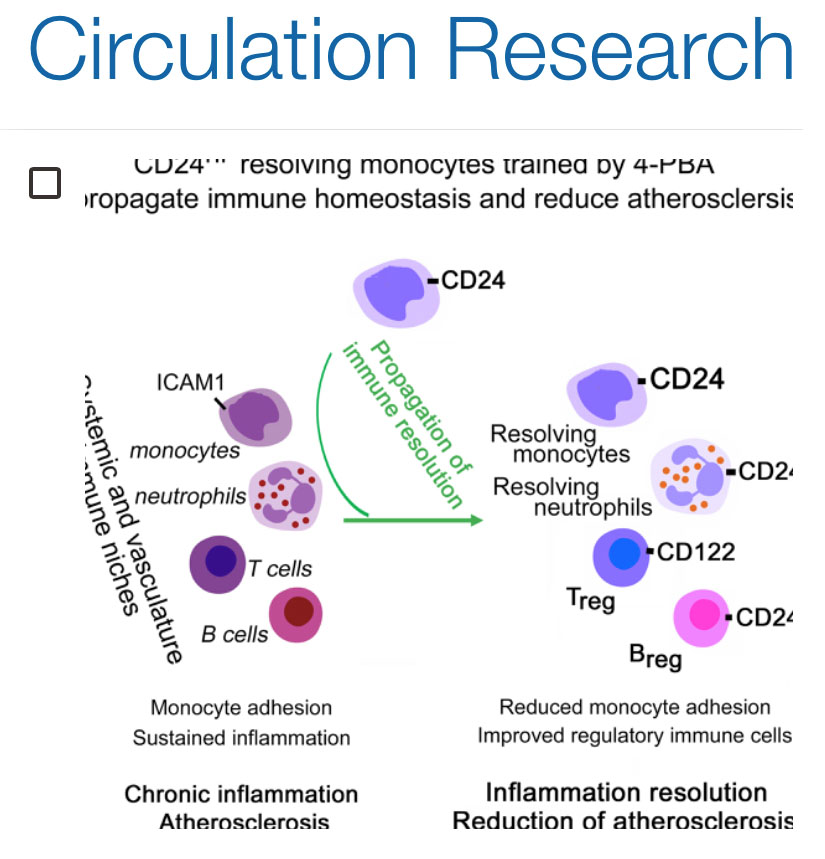
4-PBA can potently train monocytes into an inflammation-resolving state with a unique expression of CD24, enabling the propagation of resolution and homeostasis through inter-cellular communications
Transfusion of 4-PBA trained monocytes can effectively reduce atherosclerosis pathogenesis
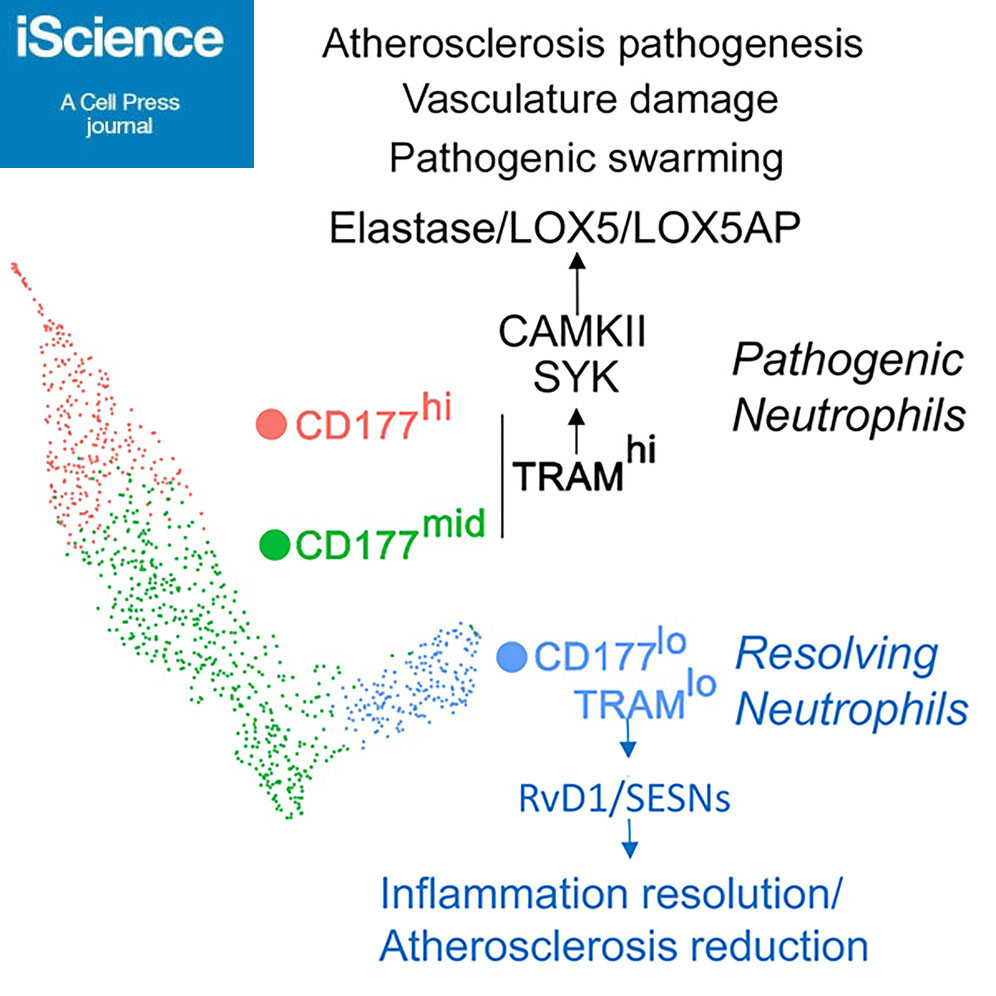
Both mice and human possess a resolving TRAM(Ticam2)lo neutrophil subset
TRAM is a stress sensor for oxLDL and free cholesterol in neutrophil inflammation
TRAM deficient neutrophils express elevated anti-inflammatory resolving mediators
Transfusion of TRAM-deleted neutrophils reduces experimental atherosclerosis
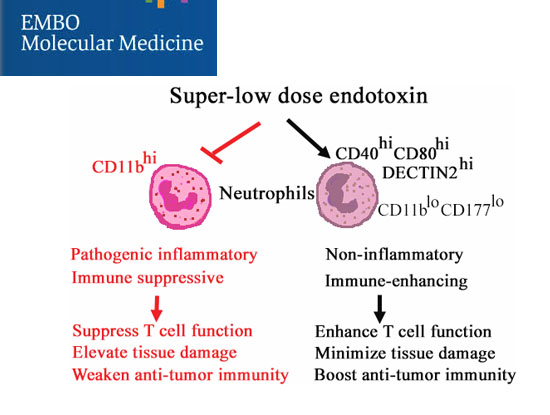
Discovery of immune enhancing neutrophils for the treatment of cancer
The immune-enhancing and less pathogenic inflammatory subset of neutrophils can be potently trained by subclinical super-low dose endotoxin
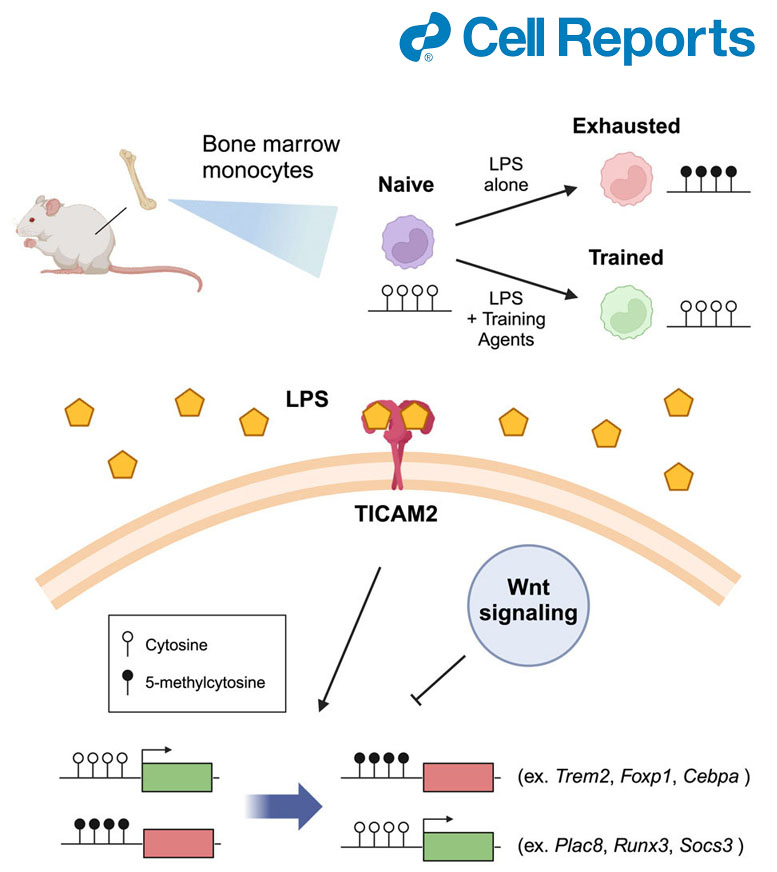
Epigenetic memory of monocyte exhaustion at DNA methylation level
Stable maintenance of monocyte exhaustion in vivo, ex vivo and in vitro
Key monocyte exhaustion signatures include:
- Reduced differentiation;
- pathogenic inflammation (elevated CD38)
- immune-suppression (Elevated PD-L1 and suppressed CD86)
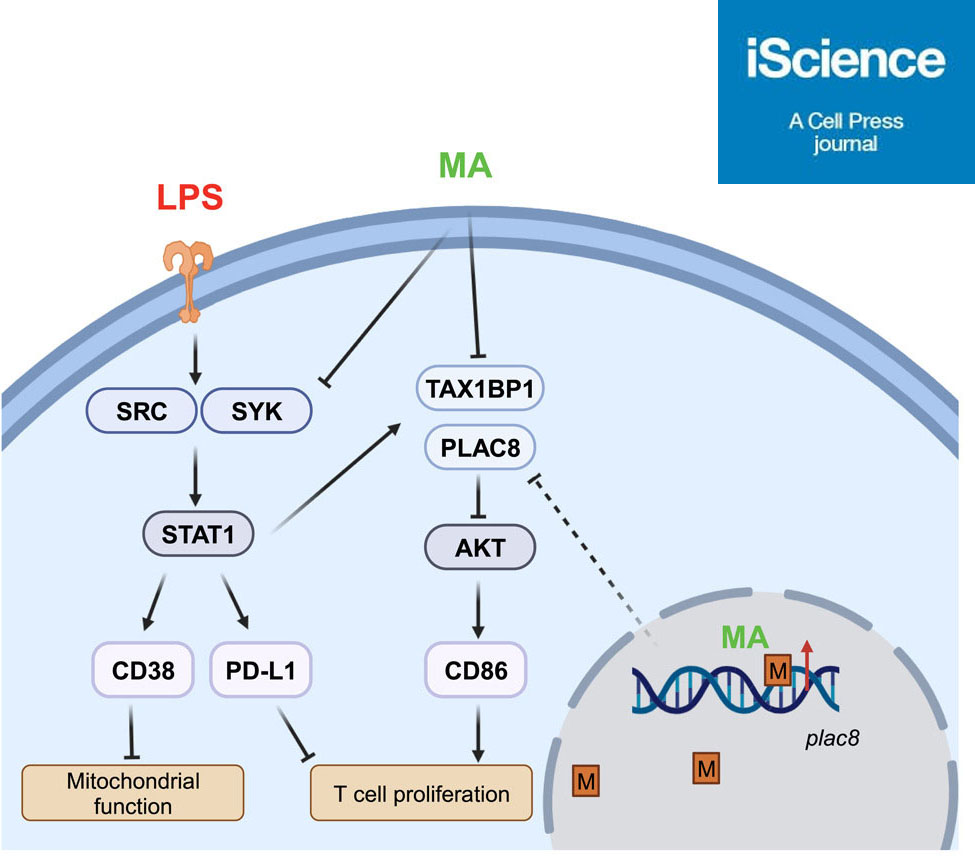
Effective intervention of monocyte exhaustion by methoxy-Mycolic Acid
- Both BCG derivative TDM or methoxy-mycolic acid can potently reduce monocyte exhaustion
- TDM or methoxy-MA blocks exacerbated STAT1/3 activation and CD38/PD-L1 expression
- TDM or MA restores AKT-mediated expression of CD86
2020s
Resolving neutrophils naturally present in human and murine systems defined, characterized by reduced CD177; reduced TRAM; elevated CD200R. Engineered resolving neutrophils can effectively be used to treat atherosclerosis.
Resolving monocytes identified with therapeutic potential in treating inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis, characterized by reduced TRAM expression and elevated levels of CD200R.
Exhaustion monocyte memory defined, with key relevance to sepsis and polymicrobial infection, initiated by sustained challenges with septic dosages of endotoxin.
The key features of exhausted monocytes include:
- a) reduced differentiation and elevated proliferative potential;
- b) pathogenic inflammation reflected by elevated expression of CD38;
- c) immune-suppression mediated by enhanced expression of PD-L1 and reduced expression of CD86.
TRAM adaptor was characterized as a key node involved in the generation of both exhaustion memory and low-grade inflammatory monocyte memory.
The generation of exhaustion memory requires TRAM-mediated disruption of mitochondria homeostasis.
The generation of low-grade inflammatory memory involves TRAM-mediated selective disruption of peroxisome homeostasis.
2010s
Low-grade inflammatory monocyte memory defined, which can be generated by sustained challenges with weak danger/damage signals.
Key principles for the generation of low-grade inflammatory memory identified that underlies the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and reduced wound healing.
Revealed key circuits underlying signal-strength and duration-dependent priming and tolerance.
Integrated computational and experimental studies revealed that the removal of homeostatic mediators is required for the generation of low-grade inflammatory memory.
TRAM adaptor is involved in the generation of low-grade inflammatory monocyte memory.
2000s
Characterized key IRAK kinases involved in endotoxin tolerance in human monocytes
- 1) IRAK-1 can be ubiquitinated following prolonged endotoxin challenge.
- 2) IRAK-1 serves as a STAT3 activating kinase, with low-signal strength mediated STAT3 activation favoring the expression of IL-6, IL-1b, while higher signal strength favoring the expression of IL-10, SLPI, and other suppressors.
- 3) IRAK-M serves as a double-edged sword, being a suppressor of low-grade inflammation by suppressing TRAM-mediated signaling, and a facilitator of monocyte exhaustion by facilitating stat1/stat3 stability .
Characterization of Tollip, a unique adaptor modulating innate immunity:
- 1) first identified its lipid binding property;
- 2) defined its homeostatic capability by facilitating lysosome fusion;
- 3) discovered its shuttling from lysosome to mitochondria which serves as a bifurcation switch for modulating homeostasis and low-grade inflammation.
1997
Human CDC14A/B phosphatases and related PTEN phosphatase discovered by Dr. Li.
